Contents of the PGA
The Program Global Area (PGA) is an essential memory structure in Oracle databases, specifically allocated for a dedicated server session. It is subdivided into various areas, each serving distinct purposes. Here’s an overview of the key contents of the PGA:
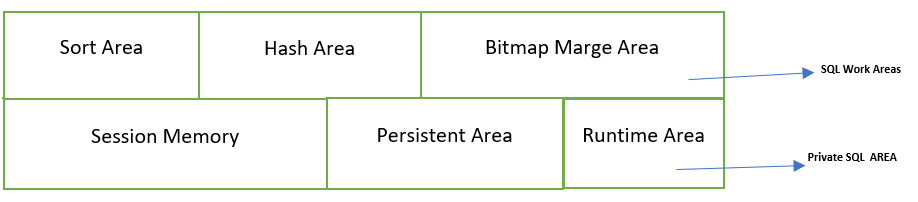
Private SQL Area
The private SQL area is crucial for storing session-specific information related to SQL statements. It includes:
- Bind Variable Values: Holds values supplied to SQL statements at runtime.
- Query Execution State Information: Tracks execution details, such as the number of rows retrieved during a full table scan.
The private SQL area is different from the shared SQL area in the SGA. Multiple sessions can share a single execution plan in the shared SQL area while maintaining separate private SQL areas for their respective executions.
A cursor acts as a pointer to a specific private SQL area. It is associated with the execution of SQL statements and can be thought of as a handle on the client side. The private SQL area is divided into two main parts:
- Run-Time Area: Created at the start of an execute request, it holds dynamic execution information, which is freed once the SQL statement is closed.
- Persistent Area: Contains bind variable values and remains allocated until the cursor is explicitly closed.
. SQL Work Areas
SQL work areas are private memory allocations within the PGA used for memory-intensive operations. They include:
- Sort Area: Used for sorting rows during query execution.
- Hash Area: A hash join operator utilizes a hash area to build a hash table from its left input.
- Bitmap Merge Area: Uses the bitmap merge area to combine data retrieved from scans of multiple bitmap indexes
